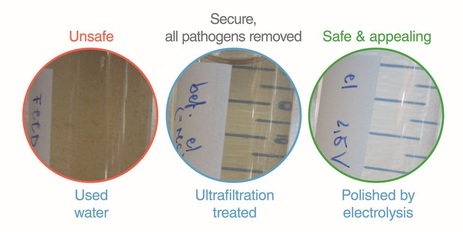
Water quality
The microbial quality of the treated water achieves drinking water quality. However, due to the accumulation of salt, the water is salty and not suitable for drinking.
We have conducted a row of experiments with the water recovery system in order to investigated its operation under stress (a varying extent of aeration and varying toilet usages which means a varying load of urine and faeces that pollute the water). It
can be concluded that the water recovery system is quite robust against
temporary changes in load. A short-term increase
in organic loading and color intensity does not compromise the hygienic quality
of the water.
However, long-term conditions of low oxygen should be avoided, as this results
in a decreased capacity (flux) and long recovery times. Learn more about the stress test in the report:
| 20130902bluediversion_eawag_waterrecovery_stresstestreport.pdf | |
| File Size: | 760 kb |
| File Type: | |
Cutting edge treatment technology with low energy requirements
The core of the water recovery processes is an ultrafiltration membrane, which is also used in large-scale drinking water production in modern cities. Ultrafiltration membranes usually require regular and energy-intensive cleaning (backflushing) to remove the biofilm that accumulates on and clogs the membrane. The ultrafiltration membrane in the Blue Diversion Toilet is maintenance free thanks to a new development in household drinking water technology, the gravity-driven membrane technology that was developed at Eawag. Higher organisms in the membrane bioreactor keep the membrane open and gravity alone is sufficient to filter the water through the membrane. Thus, the toilet requires in total 11.5W of electrical energy that is provided by a 60Wp solar panel. Compared to conventional water recovery technologies, this is a low energy requirement. It can be achieved because of the wash water receives low contamination thanks to the source-separation technology.