Field test Kampala, Uganda in 2013
|
In the first half of the test phase, the Blue Diversion Toilet
was set up in a community sanitation centre of the organization SSWARS in the informal
settlement of Kifumbira. During 3 weeks, 30 group discussions took place.
Each participant used the toilet once and the participants discussed the toilet
features in groups. 204 people gave valuable feedback.
|
|
A toilet superstructure was set up on a private property to house
the toilet during the second test phase. Over a one-month period, first
two Christian then two Muslim families shared the toilet to simulate “real
life” usage. These 22 family members were interviewed to assess their
user experiences.
|
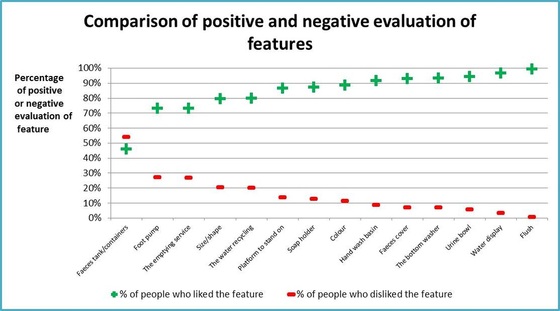
The “real world” use of the Blue Diversion Toilet allowed the behavioural scientists of Eawag to conduct a full-scale social acceptance survey with 1500 interviews. People, who received information on the toilet but did not use it showed a willingness to pay $11.50 per month per household, which is lower than the target fee of $15.50/ month. They evaluated the majority of the toilet features positively. The water features were the most positively evaluated feature, highlighting its importance to potential users.
Overall, the two-month field test was instrumental in improving the functionality of the toilet and in identifying some of the weak points that still needed rethinking and/or redesigning. The feedback and critical issues gathered during the working model test phase can be summarised in three points:
- Improve functionality of the faeces lid to better conceal previous users’ droppings
- Reduce size (height) of water wall to ensure that it fits into existing toilet superstructures
- Rethink the foot pump, which is considered too strenuous for use by children and the elderly